Non Maximum Suppression: Theory and Implementation in PyTorch (EN & CN)
Non Maximum Suppression(NMS) Is a technique used in numerous computer vision tasks. It is a class of algorithms to select one entity(e.g., bouding boxes) out of many overlapping entites. We can choose the selection criteria to arrive at the desired results. The criteria are most commonly some form of probability number and some form of overlap measure.(e.g., Intersection over Union).
非最大抑制(NMS)是一种用于众多计算机视觉任务的技术。它是一类从众多重叠实体中选择一个实体(如边界框)的算法。我们可以确定选择标准,以获得所需的结果。最常见的标准是某种形式的概率数和某种形式的重叠度量(如交集大于联合)。

Why we need it?
Before we discuss how NMS works, we must try to answer why we need it first. Most object detection algorithms use NMS to whittle down many detected bounding boxes to only a few. At the most basic level, most object detectors do some form of windowing. Thousands of windows(anchors) of various sizes and shapes are generated.
在讨论 NMS 如何工作之前,我们必须先回答为什么需要它。 大多数物体检测算法都使用 NMS 将众多检测到的边界框缩小到几个。在最基本的层面上,大多数物体检测器都会进行某种形式的窗口处理。会生成成千上万个不同大小和形状的窗口。
These windows supposedly contain only one object, and a classifier is used to obtain a probability/score for each class. Once the detector outputs a large number of bounding boxes, it is necessary to filter out the best ones. NMS is the most commonly used algorithm for this task.
这些窗口理应只包含一个物体,而分类器则用于获得每个类别的概率/分数。一旦检测器输出了大量的边界框,就有必要筛选出最好的边界框。NMS 是最常用的算法。
Intersection Over Union (IoU)
The Intersection over Union (IoU) metric, also referred to as the Jaccard index, is essentially a method used usually to quantify the percent overlap between the ground truth BBox (Bounding Box) and the prediction BBox. However, in NMS, we find IoU between two predictions BBoxes instead.
并交交集 (IoU) 度量,也称为 Jaccard 指数,本质上是一种通常用于量化真实 BBox(边界框)和预测 BBox 之间重叠百分比的方法。 然而,在 NMS 中,我们发现两个预测 BBox 之间的 IoU。
IoU in mathematical terms can be represented by the following expression,
Intersection Over Union(IoU) = (Target ∩ Prediction) / (Target U Prediction)
In our case using BBoxes, it can be modified to,
IOU(Box1, Box2) = Intersection_Size(Box1, Box2) / Union_Size(Box1, Box2)
Consider the the two BBoxes in the following figure:
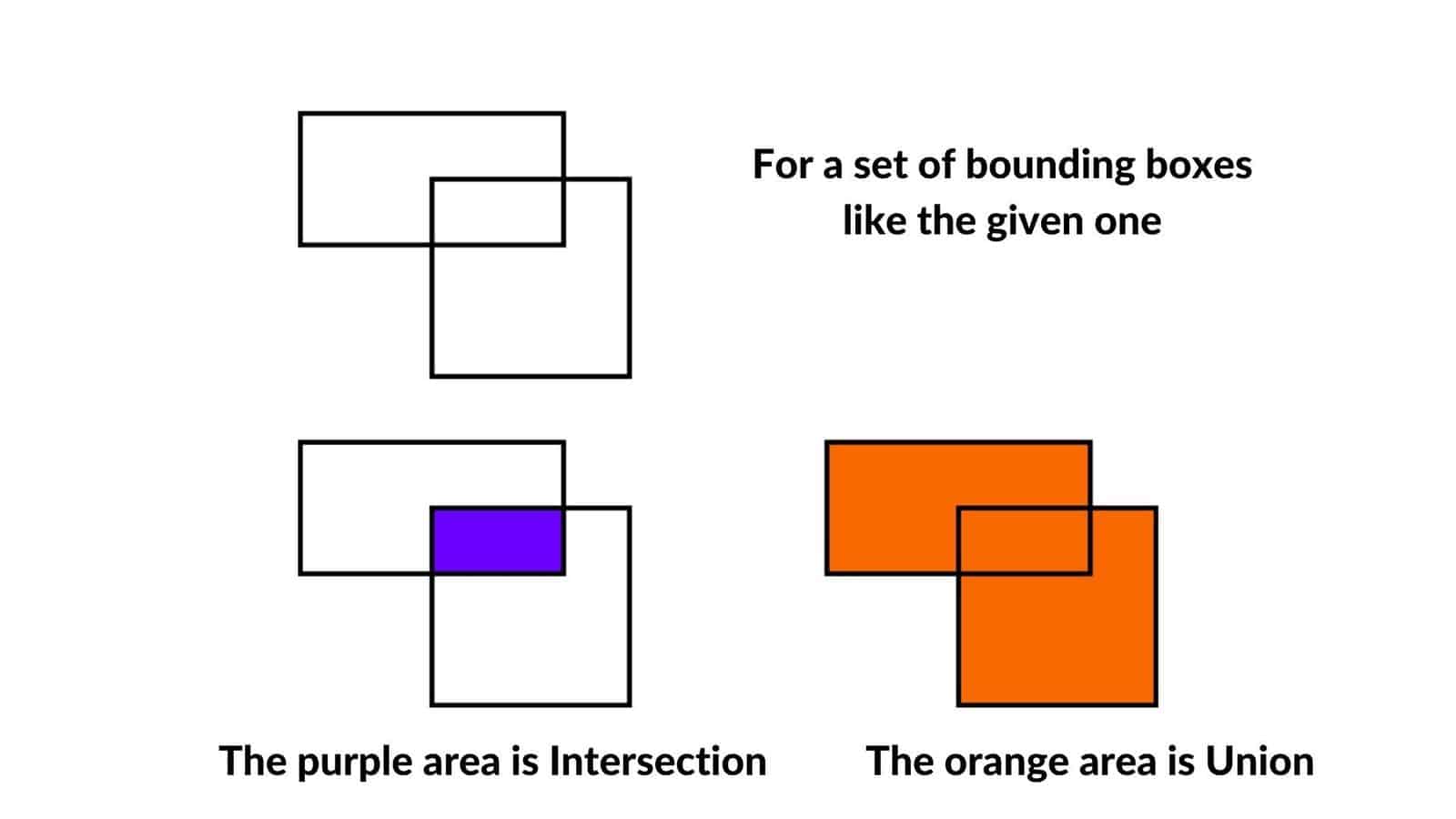 Their union area is the orange area, and their intersection area is the purple area. So the IoU can be calculated by dividing the purple area by the orange area.
Their union area is the orange area, and their intersection area is the purple area. So the IoU can be calculated by dividing the purple area by the orange area.
Implementation of IoU in Python
Let us implement this in Python so that we can use it in the later sections. Consider two BBoxes, namely Box1 having lower left coordinates as (x1,y1) and upper right coordinates as (a1,b1).
Similarly, there is another BBox, called Box2 having coordinates (x2,y2) and (a2,b2). We find their intersection box that has coordinates (xx,yy) and (aa,bb). We then use the expression discussed above to find IoU.
让我们用 Python 来实现它,以便在后面的章节中使用。考虑两个 BBox,即左下坐标为(x1,y1)、右上坐标为(a1,b1) 的 BBox1。
同样,还有一个 BBox,名为Box2,坐标为(x2,y2)和(a2,b2)。我们要找到它们的交集区,其坐标为(xx,yy)和(aa,bb)。然后我们使用上面讨论的表达式求出 IoU。
我们使用前面讨论的表达式来求出 IoU。
# find the area for the box1 (x1,y1) (a1,b1)
area1 = (a1-x1)*(b1-y1);
# find the area for the box2 (x2,y2) (a2,b2)
area2 = (a2-x2)*(b2-y2);
# Now we need to find the intersection box`
# to do that, find the largest (x, y) coordinates`
# for the start of the intersection bounding box and`
# the smallest (x, y) coordinates for the`
# end of the intersection bounding box`
xx = max(x1, x2)
yy = max(y1, y2)
aa = min(a1, a2)
bb = min(b1, b2)
# So the intersection BBox has the coordinates (xx,yy) (aa,bb)
# compute the width and height of the intersection bounding box
w = max(0, aa - xx)
h = max(0, bb - yy)
# find the intersection area
intersection_area = w*h
# find the union area of both the boxes
union_area = area1 + area2 - intersection_area
# compute the ratio of overlap between the computed
# bounding box and the bounding box in the area list
IoU = intersection_area / union_area
The NMS Algorithm
Let us get to the nitty-gritty of this post, the actual algorithm. I will divide this into three parts, what we need as input, what we get after applying the algorithm and the actual algorithm itself.
让我们进入本篇文章的重点,即实际算法。我将把它分为三个部分:我们需要的输入、应用算法后得到的结果以及实际算法本身。
Input
We get a list P of prediction BBoxes of the form (x1,y1,x2,y2,c), where (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are the ends of the BBox and c is the predicted confidence score of the model. We also get overlap threshold IoU thresh_iou.
我们得到 (x1,y1,x2,y2,c) 形式的预测 BBox 列表 P,其中 (x1,y1) 和 (x2,y2) 是 BBox 的末端,c 是模型的预测置信度得分。我们还得到重叠阈值 IoU thresh_iou。
Output
We return a list keep of filtered prediction BBoxes.
我们会返回一个经过筛选的预测 BBox 列表——keep。
Algorithm
Step 1: Select the prediction S with highest confidence score and remove it from p and add it to the final prediction list keep. (keep is empty initially).
Step 2 : Now compare this prediction S with all the predictions present in P. Calculate the IoU of this prediction S with every other predictions in P. If the IoU is greater than the threshold thresh_iou for any prediction T present in P, remove prediction T from P.
Step 3 : If there are still predictions left in P, then go to Step 1 again, else return the list keep containing the filtered predictions.
步骤 1:选择置信度最高的预测 S,将其从 p 中移除,并添加到最终预测列表 keep 中。(keep 最初为空)。
步骤 2:现在将此预测 S 与 P 中的所有的预测进行比较。计算此预测 S 与 P 中其他预测的 IoU。如果 IoU 大于 P 中任何预测值T的阈值 thresh_iou,则将预测 T 从 P 中删除。
步骤 3:如果 P 中仍有预测结果,则再次执行步骤 1,否则返回包含已过滤预测结果的列表 keep。
In layman terms, we select the predictions with the maximum confidence and suppress all the other predictions having overlap with the selected predictions greater than a threshold. In other words, we take the maximum and suppress the non-maximum ones, hence the name non-maximum suppression.
通俗地说,我们选择置信度最大的预测结果,并抑制了与所选预测结果重合度大于阈值的所有其他预测结果。换句话说,我们取最大值,抑制非最大值,因此称为非最大值抑制。
If you observe the algorithm above, the whole filtering process depends on a single threshold value thresh_iou. So selection of threshold value is vital for the performance of the model. Usually, we take its value as 0.5, but it depends on the experiment you are doing.As discussed in the NMS algorithm above, we extract the BBox of highest confidence score and remove it from P.
Now that we have a good grasp of how NMS works。
观察上面的算法,整个过滤过程取决于一个阈值 thresh_iou。因此,阈值的选择对模型的性能至关重要。通常,我们将阈值取为 0.5,但这取决于我们做的是什么实验。正如上文 NMS 算法讨论的那样,我们提取置信度得分最高的 BBox,并将其从 P 中删除。